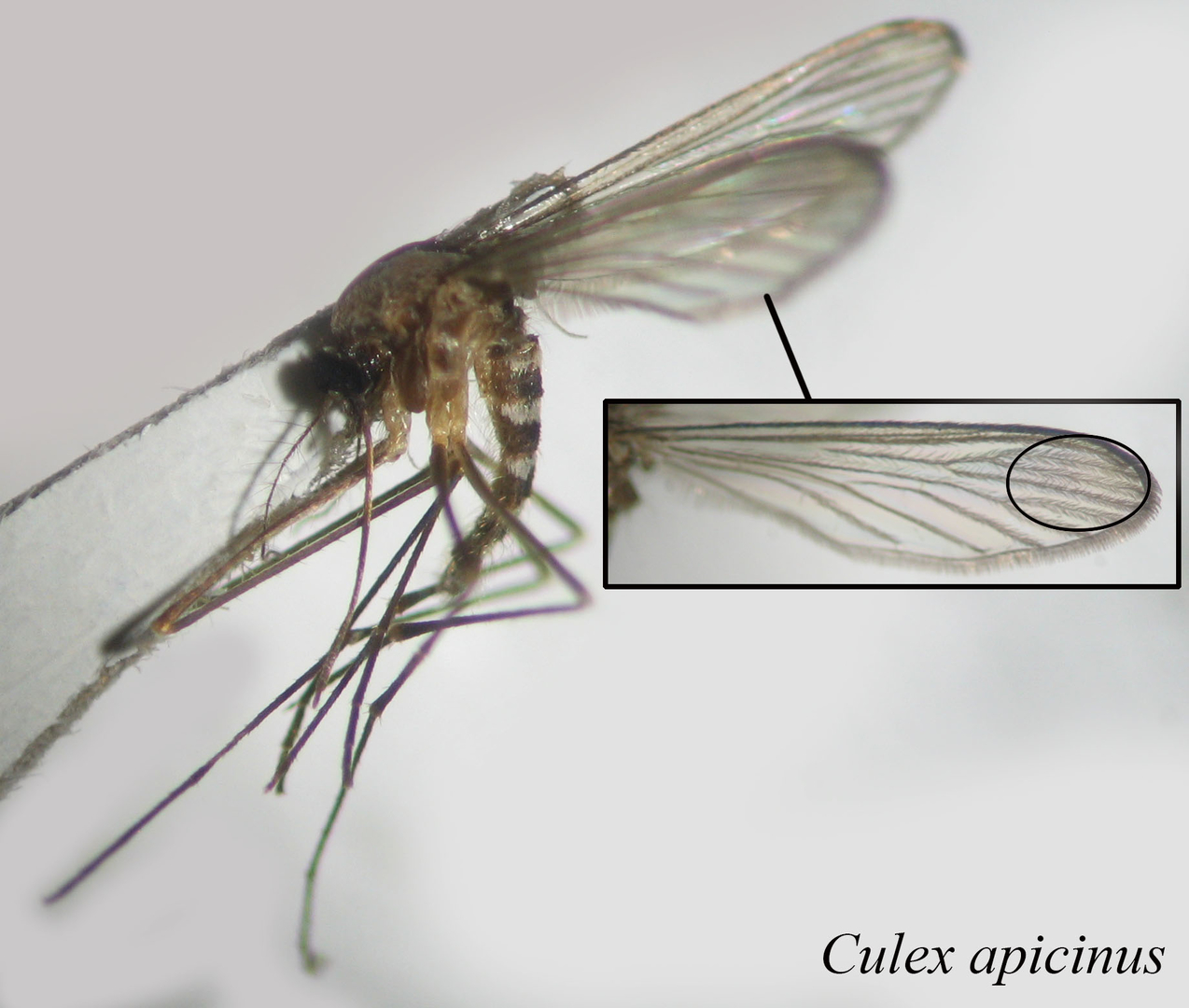
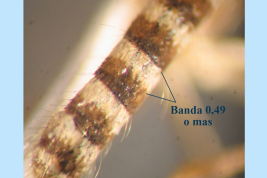
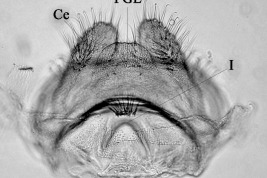
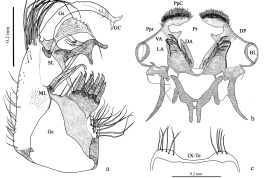
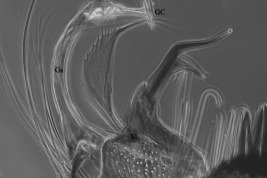
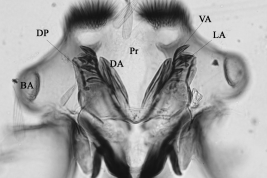
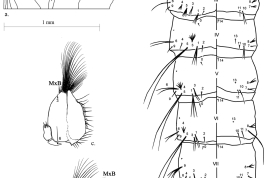
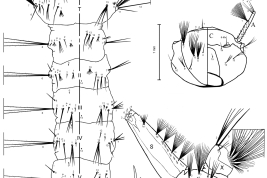
Geographic distribution
Geographic distribution
Distribution
Record
- Argentina
- Buenos Aires
- Catamarca
- Chaco
- Chubut
- Córdoba
- Corrientes
- Formosa
- Jujuy
- La Pampa
- La Rioja
- Mendoza
- Misiones
- Neuquén
- Río Negro
- Salta
- San Juan
- San Luis
- Santa Cruz
- Santa Fe
- Tucumán
- Uruguay
Other distribution
Bolivia, Chile, Peru
- alticola Martini
- debilis Dyar and Knab
- escomeli Brèthes
Culex apicinus has been listed by its synonym, Culex debilis Dyar & Knab by Martínez et al. (1961b) and Bianchini et al. 1965 (1967), according to Mitchell & Darsie(1985).
Disease relations: Culex apicinus has been found naturally infected with Saint Louis Encephalitis virus (Díaz et al. 2012).
Disease relations: Culex apicinus has been found naturally infected with Saint Louis Encephalitis virus (Díaz et al. 2012).
Immature stages were collected throughout the year except June and July from temporary to permanent, natural (pools near rivers originated by rainfalls or overflowing, stream edge, water bodies between rocks, hole in rocks) and artificial (domiciliary irrigation channels, water tanks, ditches, swimming pools) mosquito larval habitat, including water treated with chlorine sulphate. It has been molecularly detected that the species was feeding on Myiopsita monachus, Passer domesticus, Troglodytes aedon, Turdus rufiventris, and Zenaida auriculata in the temperate region of Argentina (Melgarejo-Colmenares et al., 2024).
- PHILIPPI, R. A. 1865. Aufzahlung der chileischen dipteren. Verhandllungen der Zoologish-Botanischen Gesellschaft in Wien 15: 595-596.
- LANE, J. 1953. Neotropical Culicidae. Vol. I, II. Universidade de São Paulo, Brasil. 1112 pp.
- MARTÍNEZ, A., CARCAVALLO, R. U., PROSEN, A. F. 1961b. Una nueva especie de Culex para la Argentina. Anales del Instituto de Medicina Regional, Resistencia 5 (3): 117-123.
- BIANCHINI, N., BIANCHINI, J. P., ASTEGIANO, M. 1965 (1967). Especies de mosquitos de la provincia de Córdoba (Diptera, Culicidae). Segundas Jornadas Entomoepidemiológicas Argentinas 2: 191-194.
- BRAM, R. A. 1967. Classification of Culex subgenus Culex in the New World (Diptera: Culicidae). Proceedings of the United States National Museum 120 (3557): 1-122
- MITCHELL, C. J., DARSIE, R. F. JR. 1985. Mosquitoes of Argentina. Part II. Geographic distribution and bibliography (Diptera, Culicidae). Mosquito Systematics 17 (4): 279-362.
- MITCHELL, C. J., DARSIE, R. F. JR. 1985. Mosquitoes of Argentina. Part II. Geographic distribution and bibliography (Diptera, Culicidae). Mosquito Systematics 17 (4): 279-362.
- CAMPOS, R. E., MACIÁ, A. 1998. Culicidae. Cap. 28. En Morrone, J. J. & Coscarón, S. (Eds.) Biodiversidad de Artrópodos Argentinos: Una pespectiva biotaxonómica. (pp. 291-303). La Plata, Buenos Aires, Argentina: Ediciones Sur.
- MOLINA, G. A. 2001. Nuevas citas de Culex (Culex) (Diptera: Culicidae) para el noroeste argentino. Revista de la Sociedad Entomológica Argentina 60 (1-4): 215-216.
- ROSSI, G. C., LAURITO, M., ALMIRÓN, W. R. 2008. Morphological description of the pupa and redescription of the adults and larva of Culex (Culex) apicinus Philippi (Diptera: Culicidae. Zootaxa 1941: 31-42.
- VISINTÍN, A. M., LAURITO, M., STEIN, M., RAMÍREZ, P., MOLINA, G., LORENZO, P. R., ALMIRÓN, W. R. 2010. Two new mosquito species and six new provincial records in Argentina. Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association 26 (1): 91-94.
- DIAZ, L. A., ALBRIEU-LLINÁS, G., VÁZQUEZ, A., TENORIO, A., CONTIGIANI, M. S. 2012. Silent Circulation of St. Louis Encephalitis Virus prior to an encephalitis outbreak in Córdoba, Argentina (2005). PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 6(1): e1489. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0001489
- ROSSI, G. C., MARTÍNEZ, M. 2013. Lista de especies y clave ilustrada para la identificación de larvas de mosquitos (Diptera: Culicidae) halladas criando en recipientes artificiales en Uruguay. Boletín de la Sociedad Zoológica del Uruguay (2ª época) 22 (2): 49-65.
- ROSSI, G. C. 2015. Annotated checklist, distribution, and taxonomic bibliography of the mosquitoes (Insecta: Diptera: Culicidae) of Argentina. Check List 11 (4): 1712.
- VEGGIANI AYBAR, C. A., ROSSI, G. C. 2017. Mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) of the meridional patch of the subtropical mountainous rainforest of Argentina: Update fauna and geographical distribution. Check List 13(2): 2102- doi: https://doi.org/10.15560/13.2.2102
- STECHINA, O. S., ORIA, G. O., TORRES, C., DIAZ, L. A., CONTIGIANI, M. S., STEIN, M. 2019. First detection of Madariaga virus in mosquitoes collected in a wild environment of northwestern Argentina. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 101 (4): 916-918.
- MUTTIS, E., MICIELI, M. V., BONICA, M. B., GHIRINGHELLI, P. D., GARCÍA, J. J. 2020. Mosquito Iridescent Virus: new records from nature and infections using Strelkovimermis spiculatus (Mermithidae) as a vector under laboratory conditions. Neotropical Entomology 49: 268–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-019-00755-9
- HOYOS, C. B., MONZÓN, C. M. 2021. Description of the mosquito fauna (Diptera culicidae) in the Department of Formosa, Province of Formosa. Argentine Republic. South Florida Journal of Development 2 (3): 4123-4129.
- GONZÁLEZ, C. R., REYES-VALENZUELA, C., ROSSI, G. C., LAURITO, M. 2023. Revalidation of Phalangomyia Dyar & Knab as a subgenus of Culex L. (Diptera: Culicidae) based on morphological and molecular evidence. Zootaxa doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5256.6.2
- MELGAREJO-COLMENARES, K., VEZZANI, D., GALLEGO, A., CARDO, M. V. 2024. Blood meal sources of mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) in domestic and open green environments from two urbanisations of temperate Argentina. Bulletin of Entomological Research 114: 30–40. https://doi.org/10.1017.